Features of molybdenum
What is molybdenum?
1High melting point

Molybdenum possesses the fifth highest melting point among all metals. It features a low thermal expansion coefficient and exceptional shape stability, even in high-temperature environments.
2Large electric resistance

Molybdenum has relatively high electric resistance. We offer it as a heater for high-temperature furnaces and as electrodes for lighting.
3Easy workability
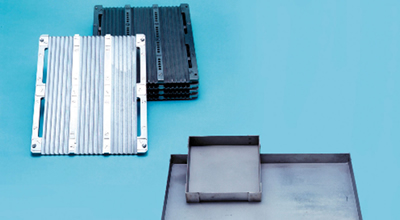
Molybdenum, which has relatively easy workability among high-melting-point metals, can be fabricated into complex shapes such as boxes and meshes.
Hard, silver-white molybdenum, named after the ore molybdenite by K. W. Schale of Sweden, is one of the rare metals. Molybdenum is often used as an additive for steel materials. Utilizing its characteristics – high melting point, excellent mechanical features, and relatively easy workability compared to tungsten – it is an indispensable metal in various applications, including ribbon and wire in the field of lighting, semiconductor substrates, glass melting electrodes, heaters and reflectors in high-temperature furnaces, and sputtering targets as wiring materials for solar cells and flat panels in power electronics.
| Atomic number *1 | 42 | |
|---|---|---|
| Element symbol | Mo | |
| Density (Mg/m3)*2 |
293K | 10.2 |
| Melting point(K)*2 | 2903±10 | |
| Boiling point(K)*2 | 5100 | |
| Electrical Resistance (10-8Ωm)*2 |
293K | 5.7 |
| Specific heat (J/kgK)*2 |
273-373K | 251 |
| Thermal conductivity (W/mK)*2 |
273-373K | 137 |
| Coefficient of Linear Expansion (10-6/K)*2 |
293-373K 293-1773K |
5.2 6.51 |
| Work function (eV)*2 |
4.2 | |
| Thermal neutron capture cross section area (barns/atom)*3 |
2.4±0.02 | |
*2 Fourth Edition of Metal Data Book, The Japan Institute of Metals and Materials
*3 Materials and techniques for electron Tubes,Walter H.Kohl (1960)
Chemical properties
- In the air, oxidation begins at room temperature and proceeds considerably at dark red temperatures.
- Molybdenum does not react at room temperature with dry oxygen, but it rapidly oxidizes at 500℃ or higher and evaporates at temperatures of 650℃ or higher, turning into MoO₃ of a white mouse color.
- It reacts easily with sulfur, carbon, or silicon at high temperatures to produce MoS₂, Mo₂C, MoSi₂, and others.
- It reacts very little at 1 atm; however, nitride can be synthesized by heating under high pressure (>15 atm).
- It has a strong affinity for arsenic.
- It exhibits little corrosion in hydrofluoric acid, hydrochloric acid, and sulfuric acid at 20℃, but shows significant corrosion in nitrate, high concentration sulfate (250℃), and aqua regia.
| Substance | Temperature | Reaction |
|---|---|---|
| Air | 200℃ | Oxidizes a little |
| ≧400℃ | Produces MoO3 | |
| Oxygen | 200℃ | Oxidizes a little |
| ≧400℃ | Produces MoO3 | |
| Vapor | ≧700℃ | Oxidizes |
| Nitrogen | ≦2,400℃ | Hardly to react (1atm) |
| Carbon monoxide | ≧1,400℃ | Produces carbides |
| Carbon dioxide | 1,200℃ | Oxidizes |
| Hydrocarbon | 1,100℃ | Carbonizes |
| Chlorine | 250℃ | Produces chloride |
| Bromine | 250℃ | Produces bromide |
| Iodine | 800℃ | No reaction |
| Hydrogen |
All temperature |
No reaction |
| Hydrogen sulfide | 1,200℃ | Produces MoS2 |
| Sulfur dioxide | 600℃ |
Produces MoO2 |
|
Nitrous oxide |
600℃ | Produces MoO3 |
| Ammonia | No reaction |
| Substance | Temperature | Reaction |
|---|---|---|
| Carbon | ≧1,100℃ | Carbonizes |
| Magnesia | 1,600℃ | Reaction |
| Zirconia | 2,200℃ | Reaction |
| Thoria | 1,900℃ | Reaction |
| Alumina | 1,900℃ | No reaction |
| Sulfur | 600℃ | Corrodes |
| Tungsten | 2,000℃ | Reaction |
| Beryllia | up to 1,900℃ | Reaction |
| Substance | Temperature | Reaction |
|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | 600℃ | Stable |
| Beryllium | Not stable | |
| Lead | up to 1,200℃ | Stable |
| Lead (with oxygen) | up to about 500℃ | Stable |
| ≧500℃ | Not stable | |
| Cesium | up to 870℃ | Stable |
| ≧870℃ | Not stable | |
| Iron | Not stable | |
| Gallium | up to 400℃ | Stable |
| Gold | Stable | |
| Potassium | up to 1,200℃ | Stable |
| Cobalt | Not stable | |
| Copper | up to 1,300℃ | Stable |
| Lithium | up to 1,400℃ | Stable |
| Magnesium | up to 1,000℃ | Stable |
| Sodium | up to 1,030℃ | Stable |
| Sodium (0.5% oxygen) | up to 400℃ | Stable |
| ≧400℃ | Not stable | |
| Nickel | Not stable | |
| Plutonium | Stable | |
| Mercury | up to 600℃ | Stable |
| ≧600℃ | Not stable | |
| Rubidium | up to 1,000℃ | Stable |
| Scandium | Not stable | |
| Rare metal | up to 1,100℃ | Stable |
| ≧1,400℃ | Not stable | |
| Silver | Stable | |
| Thallium | Not stable | |
| Uranium | Not stable | |
| Bismuth | up to 1,400℃ | Stable |
| Zinc | up to 500℃ | Stable |
| ≧500℃ | Not stable | |
| Tin | up to 520℃ | Stable |
| ≧520℃ | Not stable |
| Substance | Temperature | Reaction |
|---|---|---|
| Water |
Room |
No reaction |
| Hot liquid | No reaction | |
| 10% hydrochloric acid | Room temperature |
0.0355 * |
| Heating | 0.2794 * | |
| Dilute sulfuric acid | 110℃ | 20.1168 * |
| Concentrated sulfuric acid | 110℃ | 0.3378 * |
| 10% sulfuric acid | Room temperature |
0.0203 * |
| Heating | 0.1066 * | |
| Concentrated sulfuric acid | 110℃ | 0.2870 * |
| 10% nitric acid | Room temperature |
18.5420 * |
| Heating | 154.94 * | |
| Hydrofluoric acid | 20℃ | Hardly to react |
| 10% phosphoric acid | Room temperature |
0.1066 * |
| Heating | 0.7721 * | |
| 10% acetate | Room temperature |
0.0711 * |
| Heating | 0.2565 * | |
|
Sulfuric acid +hydrofluoric acid |
Rapidly corrodes | |
|
Sulfuric acid +hydrochloric acid |
Rapidly corrodes | |
|
Sulfuric acid +sulfuric acid |
Rapidly corrodes | |
|
Sodium hydroxide |
up to 100℃ | Stable |
| Sodium hydroxide ≧50% |
up to 100℃ | Not stable |
| Ammonium hydroxide | Not stable | |
| Potassium hydroxide ≦50% |
up to 100℃ | Stable |
| Potassium hydroxide ≧50% |
up to 100℃ | Not stable |