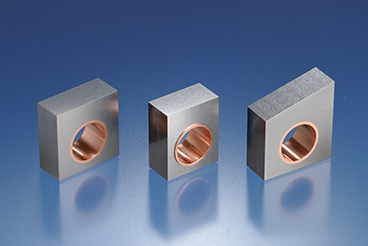
Tungsten monoblocks
"Tungsten with high thermal shock resistance."
We have developed a tungsten material suitable for the experimental fusion reactor ITER, producing a tungsten monoblock by bonding tungsten with oxygen-free copper using a specialized method. Compared to conventional materials, this innovation showed no significant surface protuberance due to deformation and maintained excellent thermal stability. It has been certified as the world's first tungsten with high thermal shock resistance, surpassing the stringent requirements set by the ITER Organization.
| Applications | Divertor of fusion reactors |
|---|
Challenge to develop "tungsten with high thermal shock resistance"
The ITER project is a global initiative to demonstrate the feasibility of fusion energy as a sustainable solution for decarbonization. For stable ITER operation, tungsten must possess excellent thermal shock resistance to endure cycles of high-temperature heating and cooling. A.L.M.T. Corp. has developed a tungsten material that suppresses the growth of recrystallized grains caused by high-temperature heating. Using this material, we fabricated a small divertor test piece and a prototype monoblock, which were tested under thermal load conditions simulating a fusion energy system. Remarkably, the prototype's performance significantly exceeded the ITER Organization's stringent requirements, earning recognition as the world's first tungsten with high thermal shock resistance.

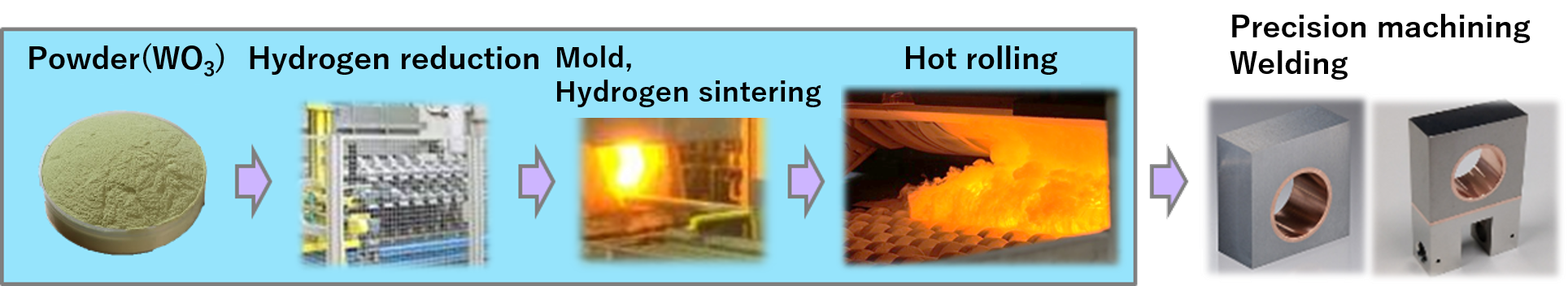
Our strength is based on integrated production from raw materials to processing
We are engaged in integrated production from powder to processed products. Leveraging this strength, we have successfully developed a new material, 'tungsten monoblock with high thermal shock resistance,' through repeated in-house trial productions, which has been highly regarded globally. Additionally, we have launched a new line utilizing robots and IoT to support mass production, achieving highly efficient production and improved quality control.

"SEI Technical Review" published Technical data
* SEI Technical Review is a technical journal that presents the technical content of the Sumitomo Electric Group.
- Tungsten technical information