Grinding wheel specifications
Specifications of diamond/CBN grinding wheels
Diamond/CBN grinding wheels (super abrasive wheels) can be applied to various specifications by combining "abrasive grain (abrasive grain type)", "grain size (abrasive grain size)", "bond strength", "degree of concentration (grain concentration in bond)", and "bond type (bonding material)". We will select the most suitable specifications for the type and shape of the work material, the required finished specifications, and the equipment istalled to.
Abrasive grains
Degree 100④Concentration B⑤Type of
Bond S40⑥Bond
Name 3.0⑦Thickness of
Abrasive Layer
①Abrasive grains
Abrasive grains of the diamond wheel are of two types: natural diamond (D) and synthetic diamond, which is often used in industrial applications. "Synthetic diamond (SD)" and "metal coated composite diamond (SDC)" are used for the grinding wheel. Also, "cubic boron nitride (CBN)" with hardness following diamond and "metal coated cubic boron nitride (CBNC)" are abrasive grains also used for the grinding wheel.
To see the whole table, scroll sideways..
| Abrasive Type | Symbol | Features | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Diamond abrasive grain | Natural diamond | D | ・The shape of abrasive grains is irregular and the crushing strength is low. ・This is rarely used at present. |
| Synthetic diamond (Friable type) ※Used mainly for resin bond. |
SD | ・Used for gridding non-ferrous materials. ・The shape of abrasive grains is irregular and the crushing strength is low. |
|
| Synthetic diamond (Blocky type) ※Mainly used for metal/vitrified bond and electroplated wheels. |
・Used for gridding non-ferrous materials. ・The shape of abrasive grains is blocky and the crushing strength is high. |
||
| Metal-coated synthetic diamond | SDC | ・Above synthetic abrasive grains coated by metal such as nickel, copper and titanium for the purpose of improving the abrasive grain holding power. | |
| CBN abrasive grain | Cubic boron nitride (Single crystalline) | CBN (BN) |
・Used for grinding ferrous materials. ・The shape of abrasive grains is blocky and the crushing strength is high. |
| Cubic boron nitride (Polycrystalline) | ・Used for grinding ferrous materials. ・The shape of abrasive grains is irregular and the crushing strength is low. |
||
| Metal-coated cubic boron nitride | CBNC (BN) |
・Above synthetic abrasive grains coated by metal such as nickel and copper for the purpose of improving the abrasive grain holding power. | |
- Synthetic Diamond
-
 Natural Diamond
Natural Diamond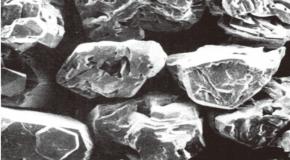 Resin Bond
Resin Bond Metal Bond
Metal Bond Coated Synthetic Diamond
Coated Synthetic Diamond
- CBN Abrasive
-
 Monocrystal
Monocrystal Polycrystal
Polycrystal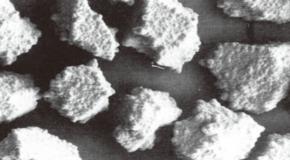 Coated Monocrystal
Coated Monocrystal
②Grit size
The grain size is the size of diamond/CBN abrasive grains (grain diameter).
The grain size and its classification method are specified by JIS (JIS B 4130).
It should be noted, however, that abrasive grains used in the super abrasive wheel are standardized up to # 325 (325/400) only. For grains finer than
# 400, the displayed grain size is not common to all manufacturers because each establishes the standard independently (or freely) and operates. For example, Company A's grain size # 10000 may not be the same as Company B’s grain size # 10000; therefore, it is necessary to check the size of abrasive grains to select the correct size.
To see the whole table, scroll sideways..
| Indicated Grain Size (Mesh) |
JIS Grain Size (Mesh) |
Average Grain Dia. (μm) |
Guide for Applicable Zone | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mesh size | 16 | 16/20 | 1190 | Rough grinding | ||
| 20 | 20/30 | 840 | ||||
| 30 | 30/40 | 590 | ||||
| 40 | 40/50 | 420 | ||||
| 50 | 50/60 | 300 | Semi-finishing | |||
| 60 | 60/80 | 250 | ||||
| 80 | 80/100 | 177 | ||||
| 100 | 100/120 | 149 | ||||
| 120 | 120/140 | 125 | ||||
| 140 | 140/170 | 105 | Finishing | |||
| 170 | 170/200 | 88 | ||||
| 200 | 200/230 | 74 | ||||
| 230 | 230/270 | 63 | ||||
| 270 | 270/325 | 50 | ||||
| 325 | 325/400 | 44 | ||||
| Micron size | 400 | The zone finer than #400 has not been standardized in JIS. | 37 | |||
| 600 | 30 | |||||
| 800 | 20 | |||||
| 1000 | 15 | |||||
| 1500 | 10 | |||||
| 2000 | 8 | |||||
| ・・・ | ・・・ | |||||
③Bond Strength
Degree of bonding is an index that shows the degree (strength and hardness) with which bonding material (bond) holds abrasive grains, and is a ranking based on N.
Generally, the harder (raising) the degree of bonding, the longer the lifetime but the lower the sharpness; the softer (lowering) the degree of bonding, the shorter the lifetime but the higher the sharpness.
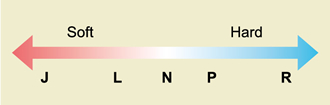
There is no rigid provision for the classification and the ranking is shown only within the same manufacturer, meaning the hardness of Company A and Company B is not the same even if the sign is the same "N." For this reason, degree of bonding may not be displayed.
* Example of abbreviation: SDC 200-100BS 40
④Degree of concentration
Degree of concentration shows the content ratio of Diamond/CBN abrasive grains (abrasive grain ratio) in the abrasive layer. When the same grain size is considered, the higher the degree of concentration, the number of abrasive grains, while the lower the degree, the lower the number of abrasive grains. It is important to select the degree of concentration most suitable for the work material.
- "4.4 cc/cm 3 = Degree of concentration 100" is defined, generally used in the range of 20 to 200.
- The three display targets: resin bond, metal bond, and vitrified bond.
- In the case of electrodeposition, which has only one abrasive grain layer, there is no degree of concentration standard.
| Concentration | Content of Abrasive Grains (ct/cm3) |
|---|---|
| 200 | 8.8 |
| 175 | 7.7 |
| 150 | 6.6 |
| 125 | 5.5 |
| 100 | 4.4 |
| 75 | 3.3 |
| 50 | 2.2 |
| 25 | 1.1 |
※1ct(カラット)=200mg
⑤Type of bond
Bonding layer to hold and combine abrasive grains in the super abrasive wheel is generally called bond. Abrasive grains drop off during processing and the other grains show up instead, that have the wheel grinding sharp. A bond most suitable for the work material and applications must be selected.
To see the whole table, scroll sideways..
| Types of Binding Materials (Bond) | Symbol | Meaning of Symbol | Main Materials of Bond | Abrasive Grain Used | Main Workpieces/Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Resin | B | Bakelite | Resin | Diamond | Cutting tool materials (cemented carbide, cermet, ceramics), metallic molds (cemented carbide) |
| CBN | Metallic molds (ferrous hardened steel, high-speed steel, die steel), surface grinding of ferrous sintered parts | ||||
| Metal | M | Metal | Metal | Diamond | Hard brittle materials (glass, ceramics, crystal, sapphire) |
| CBN | ID honing of ferrous automotive parts, cutting of ferrous bar materials | ||||
| Vitrified | V | Vitrified | Ceramics | Diamond | Cutting tool materials (sintered diamond tip, CBN tip) |
| CBN | Ferrous automotive parts, heat-resistant materials (Inconel) | ||||
| Electroplated | P(E) | Electro-plated | Plating | Diamond | Rubber, FRP, magnetic materials |
| CBN | Form grinding of ferrous automotive parts, heat-resistant materials (Inconel) |
- Please feel free to contact us
-
-
- Inquiries by email
- For emailing form
-
- Inquiries by phone
- For sales office
-